

- #FASTEST NETWORK FILE SHARING PROTOCOL SOFTWARE#
- #FASTEST NETWORK FILE SHARING PROTOCOL PC#
- #FASTEST NETWORK FILE SHARING PROTOCOL WINDOWS#
The key difference between direct-attached storage (DAS) and NAS is that DAS is simply an extension to an existing server and is not necessarily networked. NAS units rarely limit clients to a single protocol.
#FASTEST NETWORK FILE SHARING PROTOCOL WINDOWS#
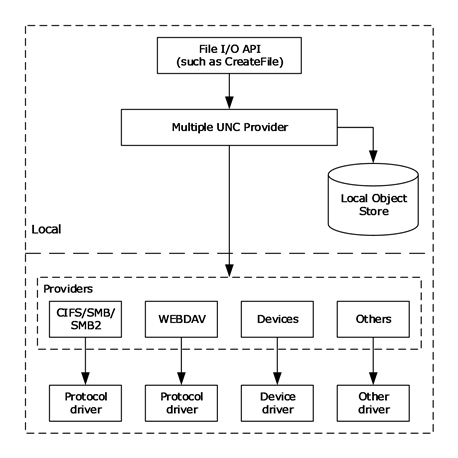
NAS uses file-based protocols such as NFS (popular on UNIX systems), SMB ( Server Message Block) (used with Microsoft Windows systems), AFP (used with Apple Macintosh computers), or NCP (used with OES and Novell NetWare). NAS systems contain one or more hard disk drives, often arranged into logical, redundant storage containers or RAID.
#FASTEST NETWORK FILE SHARING PROTOCOL PC#
For example, TrueNAS or XigmaNAS, both open source NAS solutions designed for commodity PC hardware, are implemented as a stripped-down version of FreeBSD. Ī full-featured operating system is not needed on a NAS device, so often a stripped-down operating system is used. For example, NAS units usually do not have a keyboard or display, and are controlled and configured over the network, often using a browser.
#FASTEST NETWORK FILE SHARING PROTOCOL SOFTWARE#
Although it may technically be possible to run other software on a NAS unit, it is usually not designed to be a general-purpose server.
In an appropriately configured RAID array, a single bad block on a single drive can be recovered completely via the redundancy encoded across the RAID set. In a non-RAID application, it may be important for a disk drive to go to great lengths to successfully read a problematic storage block, even if it takes several seconds. For example, some NAS versions of drives support a command extension to allow extended error recovery to be disabled. The hard disk drives with "NAS" in their names are functionally similar to other drives but may have different firmware, vibration tolerance, or power dissipation to make them more suitable for use in RAID arrays, which are often used in NAS implementations. Potential benefits of dedicated network-attached storage, compared to general-purpose servers also serving files, include faster data access, easier administration, and simple configuration. From the mid-1990s, NAS devices began gaining popularity as a convenient method of sharing files among multiple computers. They typically provide access to files using network file sharing protocols such as NFS, SMB, or AFP. Network-attached storage removes the responsibility of file serving from other servers on the network.
NAS systems are networked appliances that contain one or more storage drives, often arranged into logical, redundant storage containers or RAID. It is often manufactured as a computer appliance – a purpose-built specialized computer. NAS is specialized for serving files either by its hardware, software, or configuration. Network-attached storage ( NAS) is a file-level (as opposed to block-level storage) computer data storage server connected to a computer network providing data access to a heterogeneous group of clients.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
